This is the first known particle with four of the same kind of quark-The exotic particle could be a unique testing ground for ideas about how quarks interact
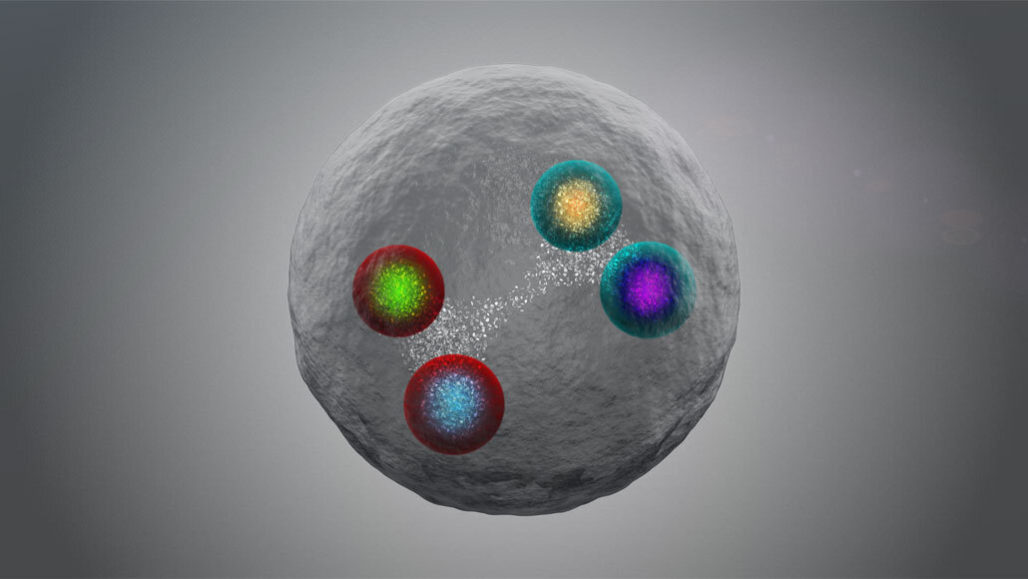
In a never-before-seen particle, four quarks of a feather flock together.
Physicists think they have detected the first conglomerate of four quarks incorporating more than two of the same kind. This tetraquark contains four quarks of the charm variety: two charm quarks and their antimatter counterparts, called anticharm quarks, researchers report online at arXiv.org on June 30.
Quarks — fundamental building blocks of matter — typically make up three-quark particles, like protons and neutrons, or quark-antiquark pairs, like pions and kaons. Physicists have observed some more exotic quark quartets (SN: 4/11/14) and even quintets (SN: 7/14/15). But the new four-quark particle, dubbed X(6900), is the first four-quark particle with all of the same type. Since charm quarks and their anticharm counterparts are among the heaviest types of quarks, it is also the first tetraquark to include more than two heavy quarks.
“It’s a pretty exciting finding,” says physicist Matthew Shepherd of Indiana University Bloomington, who wasn’t involved in the work.
Evidence of the new tetraquark was lurking in data collected from 2009 to 2018 at the Large Hadron Collider, or LHC, near Geneva. In these experiments, physicists used the LHC to smash protons together and observe the particles forged in the collisions.
The LHC data contained signatures of a particle with the mass expected for a quartet of charm quarks: around 6,900 million electron volts. That particle decayed into two J/psi particles, each containing a charm and an anticharm quark, suggesting it was originally a tetraquark with two charm and two anticharm quarks. Like other known tetraquarks, X(6900) could be either a single entity, composed of four quarks all tightly bundled together, or a pair of two-quark particles that are more loosely bound — like a set of atoms in a molecule (SN: 6/7/19).
“We need to do many kinds of checks to confirm that it’s really there,” says study coauthor Liupan An, a particle physicist at the Italian National Institute of Nuclear Physics in Florence. Those checks could include collecting more data with the LHC or seeing if other particle collision experiments produce similar results.
Assuming that the evidence for this exotic quark cluster holds up, the strange new particle offers “a sort of stress tester” for ideas about how quarks construct matter, says study coauthor Chris Parkes, a physicist at the University of Manchester in England. He compares using this tetraquark for studying particle physics to biologists looking at extremophile creatures, like tardigrades, to understand the limits of biology — or to astronomers using black holes to see whether theories about gravity hold up in such intense environments (SN: 4/16/20).
It may be easier to study quark interactions in X(6900) than its other four-quark relatives, which contain lighter quarks, Shepherd says. That’s because it’s notoriously challenging to accurately predict the complex, fast-moving behavior of light quarks. When it comes to the four heavy quarks in X(6900), on the other hand, physicists could potentially build simpler models to predict quark behavior.
source:https://www.sciencenews.org/
Comments
Post a Comment